Biotechnology definition

Biotechnology is a scientific field that uses living organisms, cells and biological systems to develop products and technologies. It combines elements of biology, chemistry, genetics and engineering to solve problems in various sectors, such as health, agriculture and the environment.
In healthcare, for example, biotechnology is used to produce drugs, vaccines and gene therapies. In agriculture, it helps create crops that are resistant to disease or harsh climatic conditions. In the environment, it can contribute to depollution or waste management. In short, it's a field of innovation that has the potential to transform our world significantly.
Genetically modified organism
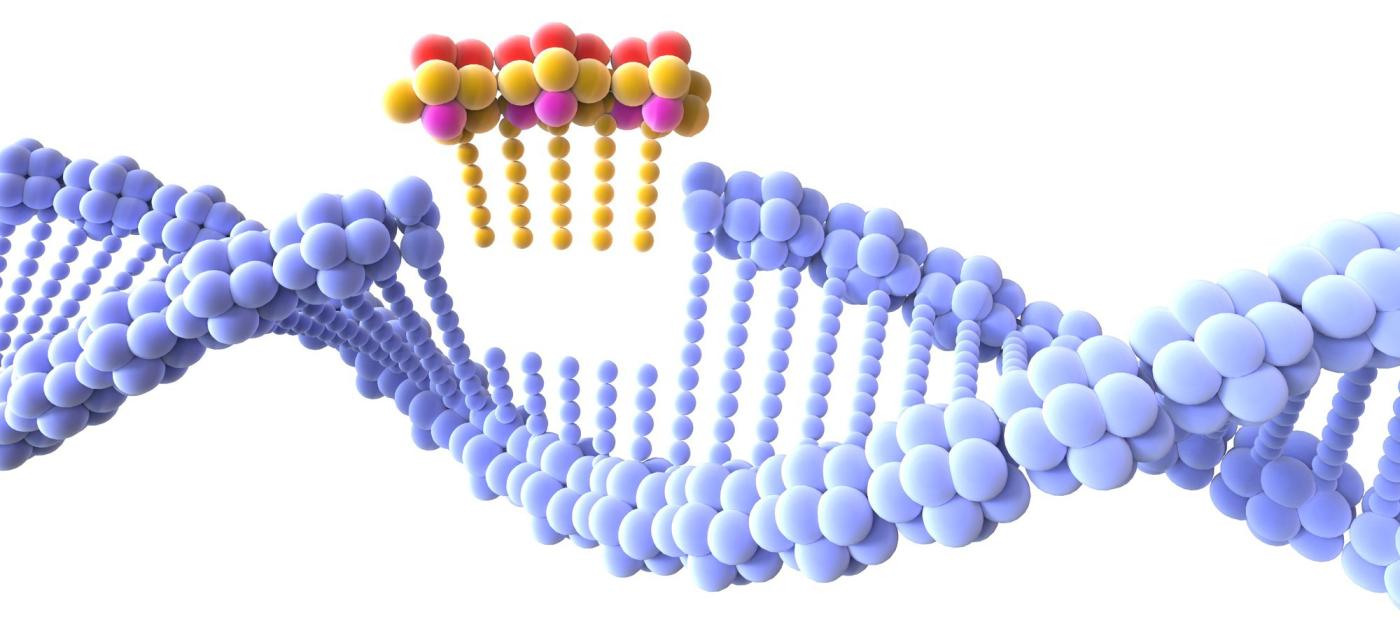
A Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) is an organism whose genetic material has been altered in an unnatural way using genetic engineering techniques. This can include the addition, deletion or modification of specific genes to confer new characteristics or traits.
GMOs are used in a variety of fields, including:
- Agriculture: To create insect-, disease- or herbicide-resistant crops, which can improve yields and reduce pesticide use.
- Medicine: to produce drugs, vaccines or gene treatments.
- Industry: to develop micro-organisms capable of producing enzymes, biofuels or other useful substances.
The use of GMOs gives rise to ethical, environmental and health-related debates, and their regulation varies from country to country.
